E-Learn Knowledge Base
What Is Cybersecurity Forensics?
Cybersecurity forensics is often referred to as digital forensics or computer forensics. It involves the investigation of cyberattacks and other illegal activities conducted in the digital space. It encompasses the identification, collection, preservation, and analysis of digital evidence, which you can use to understand the nature and extent of an attack. Crucially, you must collect and handle this evidence in a way that preserves its integrity and makes it admissible in court.
Furthermore, it’s not just limited to investigating past incidents. It plays a proactive role in enhancing an organization’s overall security posture. Additionally, cyber security forensics identifies vulnerabilities, assesses potential attack vectors, and provides recommendations on how to strengthen defenses. The goal is not only to respond to incidents but also to prevent them from happening in the first place.
Why is Cybersecurity Forensics Important?
Cybersecurity forensics is very crucial in today’s environment. With cybercriminals constantly evolving their tactics, having the capability to investigate incidents and uncover crucial evidence is vital for several reasons:
- Detecting and understanding attacks: Without cybersecurity forensics, many cyberattacks would go unnoticed or remain misunderstood. Forensics in cybersecurity helps to uncover how an attack occurred, such as the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers. Thus, this knowledge is essential for closing security gaps.
- Legal compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that require organizations to follow specific protocols when data breaches occur. Cybersecurity forensics helps ensure compliance with these legal frameworks.
- Prosecution of cybercriminals: The evidence gathered during a forensic investigation can lead to the identification and prosecution of the perpetrators.
- Damage control: Cybersecurity forensics helps organizations assess the extent of the breach, control the damage, and take appropriate action to protect sensitive information.
- Enhancing security posture: The findings from forensic investigations provide invaluable insights into vulnerabilities and can help refine security protocols.
- Mitigating future attacks: By understanding how a breach occurred, organizations can take steps to prevent similar incidents in the future. For example, if a phishing attack was the entry point for a malware infection, forensics can reveal how the email bypassed security filters. Therefore, this allows IT teams to improve their email protection systems.
- Legal evidence collection: In the event of legal action—such as prosecuting a cybercriminal or pursuing insurance claims—cybersecurity forensics provides the necessary evidence. This includes logs, malware samples, network traffic captures, and system images, all of which you can use to trace the source of the attack and identify the perpetrators.
Forensics can help identify the nature of attacks, but it is important to have systems that prevent such attacks in the first place, such as Singularity™ Endpoint Security for autonomous endpoint protection.
Key Concepts in Cybersecurity Forensics
Cybersecurity forensics follows several key concepts that guide how you can conduct investigations. These concepts ensure that your investigation is methodical and you handle evidence correctly. Additionally, they ensure that you meet legal requirements.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cyberattacks come in various forms, and cybersecurity forensics must be adaptable to handle each type. Here are some common cybersecurity threats:
- Malware is malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
- Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data, with attackers demanding payment for the decryption key.
- Phishing involves social engineering attacks that trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or financial details.
- DDoS attacks overwhelm a server or network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Insider threats are malicious or negligent actions by individuals within the organization that can lead to data breaches or system compromise.
Fundamental Principles
Several key principles underpin effective cybersecurity forensics. These principles ensure that you handle evidence correctly and remain reliable throughout the investigation.
- Data integrity: Ensuring that digital evidence remains unaltered throughout the forensic process is critical. Any changes to the data can invalidate the investigation’s findings. Forensic experts often create “hashes” (unique digital fingerprints) of files and systems to verify that no tampering has occurred.
- Chain of custody: Proper documentation of who accessed, handled, or transferred digital evidence is necessary to maintain its legal admissibility. The chain of custody is a detailed record that shows the movement of evidence from collection to court presentation.
- Confidentiality: You must protect sensitive information uncovered during an investigation from unauthorized access. This is especially important when you’re dealing with customer data, intellectual property, or national security information.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Cybersecurity forensic investigations often involve handling sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, and proprietary business data. Investigators must comply with relevant laws and regulations. Therefore, cybersecurity forensics must adhere to legal standards and ethical guidelines, including:
- Compliance with regulatory frameworks: Investigators must ensure compliance with laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the U.S., HIPAA, and others depending on the jurisdiction.
- Privacy rights: Investigations should balance the need for data collection with respect for individuals’ privacy.
- Legal admissibility: You must handle evidence collected in a way that ensures you can admit it in legal proceedings.
- Data privacy laws: Investigators must comply with regulations such as the GDPR when handling personal data. Missteps in this area can lead to hefty fines and legal issues.
- Ethical responsibility: Forensic experts must ensure that their investigations respect the privacy and rights of all individuals involved, avoiding actions that could lead to the misuse of sensitive information.
Cybersecurity Forensics Process
The cybersecurity forensics process is systematic and involves several key steps. Each step is essential for ensuring that you handle evidence properly and that the investigation yields accurate, actionable insights.
1. Incident Response
The first step in any forensic investigation is incident response. When organizations detect cyberattacks, they must act quickly to contain the threat and minimize damage. This involves identifying the affected systems, securing evidence, and preventing further damage. Key tasks during this stage include:
- Isolating infected systems: To prevent malware from spreading, organizations may disconnect infected devices or networks from the larger infrastructure.
- Initiating incident documentation: As soon as they identify an incident, investigators begin recording all actions taken and evidence collected.
2. Evidence Collection
Once the organization contains a threat, forensic investigators begin collecting digital evidence. This includes logs from firewalls, servers, endpoints, memory dumps, disk images, network traffic captures, and any other relevant data. You must collect evidence in a way that preserves its integrity, meaning that it is not altered or damaged in the process. You can use techniques like disk imaging and write blockers to create exact copies of data, ensuring that the original evidence remains untouched.
3. Data Preservation
Data preservation is critical for ensuring the collected evidence is usable throughout the investigation. Investigators create a “snapshot” of the systems involved, which they refer back to at any point in the future. The preserved data is crucial for legal proceedings, and its authenticity and integrity are tested.
4. Analysis and Examination
During this phase, forensic experts analyze the collected data to reconstruct the events that led to the breach. This includes identifying the initial point of compromise, the methods used by the attackers, and the scope of the damage. You can employ techniques like log analysis (examining system logs for abnormal activity), malware reverse engineering (dissecting malware to understand its behavior), and network traffic analysis (reviewing packet captures for malicious activity).
5. Reporting and Documentation
Finally, forensic investigators compile their findings into a detailed report. This report outlines the nature of the attack, the vulnerabilities exploited, the evidence collected, and the recommended steps for preventing future incidents. Therefore, this documentation is vital for legal purposes and the organization’s internal understanding of the incident.
Tools and Techniques
Cybersecurity forensics involves a variety of tools and techniques, each designed to help investigators gather, analyze, and interpret digital evidence.
Digital Forensic Tools
- EnCase: A widely used tool for analyzing hard drives, EnCase helps forensic experts recover deleted files, investigate malware, and create court-admissible reports.
- FTK (Forensic Toolkit): Known for its speed and efficiency, FTK is used to scan and index large volumes of data, allowing investigators to quickly search for relevant evidence.
- Wireshark: Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer that allows forensic teams to capture and analyze network traffic in real time, making it possible to detect unusual behavior or data exfiltration.
- SentinelOne: Known for its advanced cybersecurity solutions, SentinelOne provides advanced endpoint protection with integrated forensic capabilities, making it a valuable tool for incident detection and investigation. SentinelOne’s forensics capabilities allow security teams to perform deep investigations without relying on third-party tools.
Data Collection Methods
- Data acquisition: This is the process of acquiring digital evidence from devices, networks, and storage media. This can include extracting log files, accessing memory dumps, or even imaging an entire hard drive.
- Live vs. static analysis: Live analysis is conducted while a system is still running, allowing investigators to capture volatile data like running processes, active network connections, and memory contents. On the other hand, static analysis involves analyzing a snapshot or image of a system’s data after it has been shut down.
Data Analysis Techniques
- Log analysis: Investigate system and network logs to identify unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, failed login attempts, or unexpected file transfers.
- Network traffic analysis: Using tools like Wireshark, you can capture and analyze network traffic in real-time, which can reveal patterns that indicate a breach, such as large file transfers to unknown IP addresses.
- Malware analysis: This involves disassembling or reverse-engineering malicious software to understand its functionality and impact. There are two types of malware analysis: static (analyzing the code without executing it) and dynamic (executing the code in a controlled environment to observe its behavior).
Types of Cybersecurity Forensic Investigations
Cybersecurity forensics can be divided into several categories depending on the type of system you are investigating.
1. Computer Forensics
This involves examining computers, servers, and storage devices to find evidence of cyberattacks. Investigators might look at deleted files, system logs, or malware left behind by the attacker.
2. Network Forensics
In network forensics, investigators analyze network traffic and logs to identify malicious activities, such as data breaches or DDoS attacks.
3. Mobile Device Forensics
Mobile devices have become a target for attackers due to the wealth of personal and corporate data they store. Forensics of mobile devices involves recovering data from smartphones and tablets to determine the source and nature of an attack.
4. Cloud Forensics
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud services, cloud forensics has become crucial. Investigating cyberattacks in the cloud involves unique challenges due to the distributed nature of data and the involvement of third-party service providers.
Challenges in Cybersecurity Forensics
Cybersecurity forensics faces several significant challenges that can hinder investigations and the ability to respond effectively to cyberattacks. Some of these challenges include:
#1. Encryption and Data Hiding
Encryption transforms your data and locks it out by requiring a decryption key. But cyber adversaries can take it a step further by changing file extensions, hiding file attributes, and inserting bit-shifting into the mix. They may fragment the evidence or hide entire file partitions to make cracking down cases difficult.
Investigators can only access these contents with the proper decryption keys. In some cases, breaking encryption can be virtually impossible, leaving critical evidence out of reach. Sometimes, even if you have the keys, it’s still hard to sort the evidence because of how perpetrators have tampered with it.
#2. Anti-Forensics Techniques
Attackers are getting smarter and use advanced anti-forensics techniques to erase their digital footprints. These techniques include wiping off log files, deleting malware traces, using encryption to hide data, and employing rootkits to evade detection. Anti-forensics tools are designed to destroy or alter data in ways that can prevent investigators from gathering meaningful evidence. They add more layers of complexities to cybersecurity forensics processes.
#3. Volatile Data Analysis
Many forms of critical evidence exist only in volatile memory, such as RAM, which is lost when a system is powered off. This creates a significant challenge for forensic experts, who must capture this volatile data before it disappears. Without proper incident response procedures in place, valuable data such as running processes, active network connections, and session information can be lost, hindering the investigation.
#4. Cross-Jurisdictional Issues
Cybercrimes often cross national borders, and forensic investigations must navigate the complexities of varying international laws and regulations. What may be considered legal in one jurisdiction could violate the laws of another. Investigators must work within different legal frameworks, sometimes requiring international cooperation to collect evidence, access data, or apprehend suspects. This can slow down investigations and create obstacles in evidence collection, particularly when cooperation between countries is limited.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Forensics
To enhance the effectiveness of cybersecurity forensics and address the challenges involved, organizations should adopt several best practices. These best practices ensure that forensic investigations are thorough, legally compliant, and useful in both preventing and responding to cyberattacks.
1. Incident Readiness
One of the most critical components of effective cybersecurity forensics is incident readiness. Organizations need to be prepared in advance for cyber incidents by implementing robust policies and procedures and ensuring that staff are trained in incident response and forensic techniques.
- Policies and procedures: Organizations should establish detailed incident response service and forensic investigation policies that outline the steps to take following a cyberattack. These procedures should include proper data collection methods, preservation techniques, and guidelines for handling digital evidence. Regular audits and drills can help ensure that all employees understand their roles during a security incident.
- Training and awareness: IT and security teams must be well-versed in forensic tools, data-handling procedures, and legal requirements. Investing in regular training ensures that employees remain up to date with the latest threats and investigative techniques. Training sessions and incident response drills can simulate real-world scenarios, helping the team build readiness and confidence in handling cyber incidents.
2. Collaborative Efforts
In today’s interconnected world, collaboration is key to effective cybersecurity forensics. Public-private partnerships and international cooperation can help organizations strengthen their defenses and improve their ability to investigate cyberattacks.
- Public-private partnerships: Governments, law enforcement agencies, and private organizations must work together to share intelligence, best practices, and forensic tools. Thus, by collaborating with public entities like the FBI or CERTs (Computer Emergency Response Teams), private organizations can gain access to threat intelligence, incident response resources, and legal expertise. Therefore, this collaboration can enhance their ability to respond to sophisticated cyberattacks.
- International cooperation: What will you do if a criminal attacks your organization from overseas? It may lie outside the jurisdiction of your state. This is where international cyber investigations come into play. In many such cases, international law enforcement agencies tie up with cybersecurity groups and coordinate efforts to solve incidents. Their joint investigations expedite the process of obtaining evidence, tracking down cybercriminals, and prosecuting offenders.
Register for this course: Enrol Now
What is application security (AppSec)?
Application security refers to the process of identifying and repairing vulnerabilities in application software—from development to deployment—to prevent unauthorized access, modification, or misuse.
Application security (AppSec) is an integral part of software engineering and application management. It addresses not only minor bugs but also prevents serious application vulnerabilities from being exploited. An ongoing process rather than a single technology, application security (AppSec) is a crucial component of cybersecurity, encompassing practices that prevent unauthorized access, data breaches and code manipulation of application software. As applications have become more complex, AppSec has become increasingly important and challenging. This evolution necessitates new approaches in secure software development. DevOps and security practices must take place in tandem, supported by professionals with a deep understanding of the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
At its core, application security aims to safeguard sensitive data and application code from theft or manipulation. This involves implementing security measures during application development and design phases and maintaining protection during and post-deployment.
Ranging from hardware safeguards like routers to software-based defenses such as application firewalls, these measures are supplemented by procedures including regular security testing routines. Additional methods, like thorough code reviews and analysis tools, identify and mitigate vulnerabilities within the codebase. Defensive measures such as strong authentication mechanisms and encryption techniques protect against unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Regular security assessments and penetration testing further ensure proactive vulnerability management.
Organizations use various strategies for managing application security depending on their needs. Factors such as cost, expertise, and the specific challenges posed by different environments (e.g., cloud security, mobile app security, and web application security for apps accessed through a browser interface) influence their methods. Some organizations choose to manage application security internally, which enables direct control over processes and tailored security measures by in-house teams.
When not managed on-premises, organizations outsource application security—a part of managed security services (MSS)—to a managed security service provider (MSSP). An MSSP can provide a sophisticated security operations center (SOC), security information and event management (SIEM) solutions and access to specialized skills and application security tools. These can benefit organizations that lack internal resources and expertise. Whether managed internally or outsourced, strong security measures are essential to safeguard applications against evolving cyber threats and vulnerabilities
Why is application security important?
Application security is important for any organization handling customer data, as data breaches pose significant risks. Implementing a strong application security program is crucial to mitigating these application security risks and reducing the attack surface. Developers strive to minimize software vulnerabilities to deter attackers targeting valuable data—whether it's customer information, proprietary secrets or confidential employee data—for nefarious purposes.
In today's cloud-based landscape, data spans various networks and connects to remote servers. Network monitoring and security is vital, but safeguarding individual applications is equally important. Hackers increasingly target applications, making application security testing and proactive measures indispensable for protection. A proactive approach to application security offers an edge by enabling organizations to address vulnerabilities before they impact operations or customers.
Neglecting application security can have serious consequences. Security breaches are prevalent and can lead to temporary or permanent business shutdowns. Customers entrust organizations with their sensitive information, expecting it to be kept safe and private. Failure to secure applications can result in identity theft, financial loss, and other privacy violations. These failures undermine customer trust and damage the organization’s reputation. Investing in the right application security solutions is essential to protect both organizations and their customers from potential harm.
Types of application security
Application security encompasses various features aimed at protecting applications from potential threats and vulnerabilities. These include:
Authentication: Implemented by developers to verify the identity of users accessing the application. Authentication ensures that only authorized individuals gain entry, sometimes requiring multifactor authentication, a combination of factors like passwords, biometrics or physical tokens.
Authorization: Following authentication, users are granted permission to access specific functionalities based on their validated identity (identity access management). Authorization verifies user privileges against a predefined list of authorized users, ensuring access control.
Encryption: Applied to safeguard sensitive data during transmission or storage within the application. Particularly crucial in cloud-based environments, encryption obscures data, preventing unauthorized access or interception.
Logging: Vital for tracking application activity and identifying security breaches, application log files chronicle user interactions. Logging provides a timestamped record of accessed features and user identities, which is helpful for post-incident analysis.
Testing: Essential to validate the effectiveness of security measures. Through various testing methods such as static code analysis and dynamic scanning, vulnerabilities are identified and addressed to ensure strong security controls.
Application security benefits
Application security offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
Decreased disruption: Business operations can be disrupted by security issues. Ensuring application security minimizes the risk of service interruptions that lead to costly downtime.
Early awareness of issues: Strong application security identifies common attack vectors and risks during the app development phase, enabling resolution before the app is launched. After deployment, the application security solution can identify vulnerabilities and alert administrators to potential issues.
Enhanced customer confidence: Applications with a reputation for security and trustworthiness help increase customer confidence in the brand, which can improve brand loyalty.
Improved compliance: Application security measures help organizations comply with regulatory and compliance requirements related to data security, such as GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS. This helps the organization avoid compliance-related penalties, fines and legal issues.
Increased cost savings: Investing in application security in the development process can lead to long-term cost savings. Fixing security issues early in this phase is usually more cost-effective than addressing them after deployment. In addition, strong app security helps avoid the financial costs associated with data breaches, including investigations, legal fees and regulatory fines.
Prevention of cyberattacks: Applications are frequent targets for cyberattacks including malware and ransomware, SQL injections and cross-site scripting attacks. Application security measures help organizations prevent these attacks or minimize their impact.
Protection of sensitive data: Robust security measures help organizations maintain confidentiality and integrity by safeguarding sensitive data such as customer information, financial records and intellectual property from unauthorized access, modification, or theft.
Reduced risks: Eliminating vulnerabilities increases the potential to ward off attacks. Proactive application security measures such as code reviews, security testing, and patch management reduce the likelihood of security incidents and minimize the impact of potential breaches.
Support of brand image: A security breach can erode customer trust in an organization. By prioritizing application security, organizations demonstrate their commitment to maintaining trust and protecting customer data, which helps retain customers and attract new ones.
The application security process
The application security process involves a series of essential steps aimed at identifying, mitigating and preventing security vulnerabilities.
Risk assessment and planning
This initial phase involves identifying potential security risks specific to the application through thorough threat modeling. It includes assessing the application's functionality, data handling processes and potential attack vectors. Based on this assessment, a security plan is developed to outline measures needed to mitigate identified risks.
Secure design and development
During the design and development phase, security considerations are integrated into the application architecture and coding practices. Development teams follow secure coding guidelines and application security best practices to minimize the introduction of vulnerabilities into the codebase. This includes implementing input validation, authentication mechanisms, proper error handling and establishing secure deployment pipelines.
Code review and testing
Comprehensive code reviews and testing are conducted to identify and address security vulnerabilities in the application code. This involves both static code analysis to identify potential flaws in the source code and dynamic testing to simulate real-world attack scenarios and assess the application's resilience to exploitation.
Security testing and evaluation
Security testing is performed to assess the effectiveness of implemented security controls and identify any remaining vulnerabilities. This happens primarily through red teaming, with capabilities like penetration testing , vulnerability scanning, and security risk assessments. This testing identifies weaknesses in the application's defenses and ensures compliance with security standards and regulations.
Deployment and monitoring
Once the application is ready for deployment, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are necessary to ensure continued security. This includes implementing logging and monitoring mechanisms to quickly detect and respond to security incidents. Regular security updates and patches are also applied to address newly discovered vulnerabilities and mitigate emerging threats.
Application security testing (AST) and tools
Developers perform application security testing (AST) as part of the software development process to ensure there are no vulnerabilities in a new or updated version of a software application. Some of the tests and tools related to application security are:
Static application security testing (SAST): This AST uses solutions that analyze application source code without executing the program. SAST can identify potential security vulnerabilities, coding errors and weaknesses in the application's codebase early in the development lifecycle. Developers can then fix these issues before deployment.
Dynamic application security testing (DAST): Unlike SAST, DAST tools evaluate applications while they are running. They provide insights into the security posture of applications in production environments, simulating real-world attack scenarios to identify vulnerabilities such as input validation errors, authentication flaws and configuration weaknesses that attackers could exploit.
Interactive application security testing (IAST): IAST combines SAST and DAST and improves them by focusing on dynamic and interactive testing, inspecting the application using actual user inputs and actions in a controlled and supervised environment. Vulnerabilities are reported in real time.
OWASP top ten: The OWASP top ten is a list of the top ten most critical security risks facing web applications. Compiled by the Open Web Applications Security Project (OWASP), an international nonprofit organization focused on improving software security, the list provides periodically updated guidance to developers, security professionals and organizations on the most prevalent and impactful vulnerabilities that can lead to security breaches.
Runtime application self-protection (RASP): RASP solutions protect applications at runtime by monitoring and observing behavior for signs of suspicious or malicious activity. They can detect and respond to attacks in real time, and some forms of RASP can block malicious actions when they are detected.
Software composition analysis (SCA): SCA tools identify and manage open-source components and third-party libraries used in an application. They analyze dependencies and assess their security posture, including known vulnerabilities and licensing and compliance issues.
Secure development lifecycle (SDL) tools: SDL tools integrate security into the development process. They provide developers with guidelines and automated checks to ensure security considerations are addressed throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
Web application firewalls (WAFs): WAFs are designed to protect web applications and their APIs by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet at the application layer. They can detect and block common web-based attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). This enables risk mitigation of data breaches and unauthorized access.
These tools and technologies, along with others such as encryption, authentication mechanisms and security testing frameworks, are important for protecting applications from a wide range of security threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations often employ a combination of these tests and tools as part of their application security strategy.
Register for this course: Enrol Now
What is social engineering
Social engineering is the term used for a broad range of malicious activities accomplished through human interactions. It uses psychological manipulation to trick users into making security mistakes or giving away sensitive information.
Social engineering attacks happen in one or more steps. A perpetrator first investigates the intended victim to gather necessary background information, such as potential points of entry and weak security protocols, needed to proceed with the attack. Then, the attacker moves to gain the victim’s trust and provide stimuli for subsequent actions that break security practices, such as revealing sensitive information or granting access to critical resources.
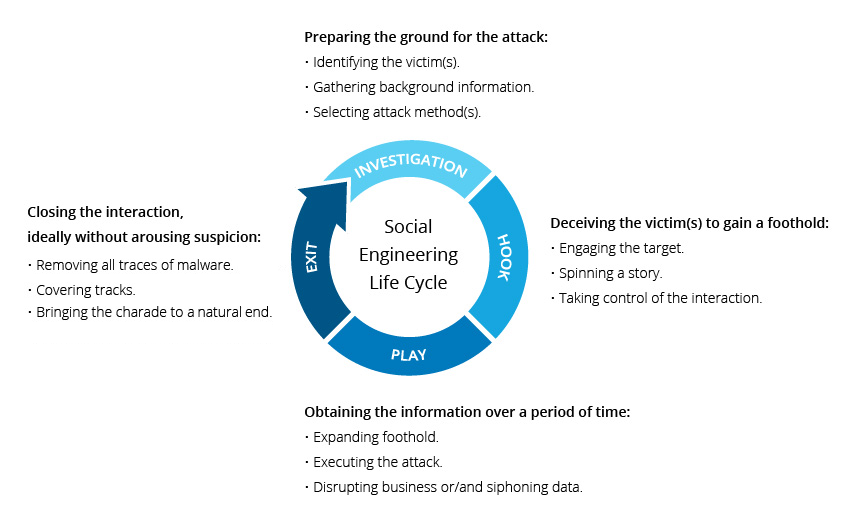
Social Engineering Attack Lifecycle
What makes social engineering especially dangerous is that it relies on human error, rather than vulnerabilities in software and operating systems. Mistakes made by legitimate users are much less predictable, making them harder to identify and thwart than a malware-based intrusion.
Social engineering attack techniques
Social engineering attacks come in many different forms and can be performed anywhere where human interaction is involved. The following are the five most common forms of digital social engineering assaults.
Baiting
As its name implies, baiting attacks use a false promise to pique a victim’s greed or curiosity. They lure users into a trap that steals their personal information or inflicts their systems with malware.
The most reviled form of baiting uses physical media to disperse malware. For example, attackers leave the bait—typically malware-infected flash drives—in conspicuous areas where potential victims are certain to see them (e.g., bathrooms, elevators, the parking lot of a targeted company). The bait has an authentic look to it, such as a label presenting it as the company’s payroll list.
Victims pick up the bait out of curiosity and insert it into a work or home computer, resulting in automatic malware installation on the system.
Baiting scams don’t necessarily have to be carried out in the physical world. Online forms of baiting consist of enticing ads that lead to malicious sites or that encourage users to download a malware-infected application.
Scareware
Scareware involves victims being bombarded with false alarms and fictitious threats. Users are deceived to think their system is infected with malware, prompting them to install software that has no real benefit (other than for the perpetrator) or is malware itself. Scareware is also referred to as deception software, rogue scanner software and fraudware.
A common scareware example is the legitimate-looking popup banners appearing in your browser while surfing the web, displaying such text such as, “Your computer may be infected with harmful spyware programs.” It either offers to install the tool (often malware-infected) for you, or will direct you to a malicious site where your computer becomes infected.
Scareware is also distributed via spam email that doles out bogus warnings, or makes offers for users to buy worthless/harmful services.
Pretexting
Here an attacker obtains information through a series of cleverly crafted lies. The scam is often initiated by a perpetrator pretending to need sensitive information from a victim so as to perform a critical task.
The attacker usually starts by establishing trust with their victim by impersonating co-workers, police, bank and tax officials, or other persons who have right-to-know authority. The pretexter asks questions that are ostensibly required to confirm the victim’s identity, through which they gather important personal data.
All sorts of pertinent information and records is gathered using this scam, such as social security numbers, personal addresses and phone numbers, phone records, staff vacation dates, bank records and even security information related to a physical plant.
Phishing
As one of the most popular social engineering attack types, phishing scams are email and text message campaigns aimed at creating a sense of urgency, curiosity or fear in victims. It then prods them into revealing sensitive information, clicking on links to malicious websites, or opening attachments that contain malware.
An example is an email sent to users of an online service that alerts them of a policy violation requiring immediate action on their part, such as a required password change. It includes a link to an illegitimate website—nearly identical in appearance to its legitimate version—prompting the unsuspecting user to enter their current credentials and new password. Upon form submittal the information is sent to the attacker.
Given that identical, or near-identical, messages are sent to all users in phishing campaigns, detecting and blocking them are much easier for mail servers having access to threat sharing platforms.
Spear phishing
This is a more targeted version of the phishing scam whereby an attacker chooses specific individuals or enterprises. They then tailor their messages based on characteristics, job positions, and contacts belonging to their victims to make their attack less conspicuous. Spear phishing requires much more effort on behalf of the perpetrator and may take weeks and months to pull off. They’re much harder to detect and have better success rates if done skillfully.
A spear phishing scenario might involve an attacker who, in impersonating an organization’s IT consultant, sends an email to one or more employees. It’s worded and signed exactly as the consultant normally does, thereby deceiving recipients into thinking it’s an authentic message. The message prompts recipients to change their password and provides them with a link that redirects them to a malicious page where the attacker now captures their credentials.
Social engineering prevention
Social engineers manipulate human feelings, such as curiosity or fear, to carry out schemes and draw victims into their traps. Therefore, be wary whenever you feel alarmed by an email, attracted to an offer displayed on a website, or when you come across stray digital media lying about. Being alert can help you protect yourself against most social engineering attacks taking place in the digital realm.
Moreover, the following tips can help improve your vigilance in relation to social engineering hacks.
- Don’t open emails and attachments from suspicious sources – If you don’t know the sender in question, you don’t need to answer an email. Even if you do know them and are suspicious about their message, cross-check and confirm the news from other sources, such as via telephone or directly from a service provider’s site. Remember that email addresses are spoofed all of the time; even an email purportedly coming from a trusted source may have actually been initiated by an attacker.
- Use multifactor authentication – One of the most valuable pieces of information attackers seek are user credentials. Using multifactor authentication helps ensure your account’s protection in the event of system compromise.
- Be wary of tempting offers – If an offer sounds too enticing, think twice before accepting it as fact. Googling the topic can help you quickly determine whether you’re dealing with a legitimate offer or a trap.
- Keep your antivirus/antimalware software updated – Make sure automatic updates are engaged, or make it a habit to download the latest signatures first thing each day. Periodically check to make sure that the updates have been applied, and scan your system for possible infections.
Register for this course: Enrol Now
What is open source intelligence (OSINT)?
Open source intelligence (OSINT) is the process of gathering and analyzing publicly available information to assess threats, make decisions or answer specific questions.
Many organizations use OSINT as a cybersecurity tool to help gauge security risks and identify vulnerabilities in their IT systems. Cybercriminals and hackers also use OSINT techniques for social engineering, phishing and exposing targets for cyberattacks.
Beyond cybersecurity, other disciplines such as law enforcement, national security, marketing, journalism and academic research can also use open source intelligence.
How OSINT works
As far back as World War II, highly trained agents in the intelligence community have monitored open source information such as radio broadcasts, newspapers and market fluctuations. Today, given the number and variety of easily accessible data sources, nearly anyone can participate in open source intelligence gathering.
Some of the public sources from which OSINT researchers collect data points include:
-
Internet search engines such as Google, DuckDuckGo, Yahoo, Bing and Yandex.
-
Print and online news media including newspapers, magazines and news sites.
-
Social media accounts on platforms such as Facebook, X, Instagram and LinkedIn.
-
Online forums, blogs and Internet Relay Chats (IRC).
-
The dark web, an encrypted area of the internet that is not indexed by search engines.
-
Online directories of phone numbers, email addresses and physical addresses.
-
Public records including births, deaths, court documents and business filings.
-
Government records such as meeting transcripts, budgets, speeches and press releases issued by local, state and federal and national governments.
-
Academic research including papers, theses and journals.
-
Technical data such as IP addresses, APIs, open ports and web page metadata.
However, before data collection from OSINT sources begin, a clear objective should be established. For example, security professionals who use OSINT first determine which insights they seek to uncover, and which public data will yield the wanted results.
After the public information is collected, it must then be processed to filter out unnecessary or redundant data. Security teams can then analyze the refined data and create an actionable intelligence report.
How hackers use OSINT
Threat actors often use OSINT to uncover sensitive information they can leverage to exploit vulnerabilities in computer networks.
These information can include personal details about an organization’s employees, partners and vendors that are easily accessible on social media and company websites. Or technical information such as credentials, security gaps or encryption keys that might appear in the source code of web pages or cloud applications. There are also public websites that publish compromising information such as stolen logins and passwords from data breaches.
Cybercriminals are able to use this public data for various nefarious purposes.
For example, they might use personal information from social networks to create tailored phishing emails that convince readers to click on a malicious link. Or conduct a Google search with specific commands that reveal security weaknesses in a web application, a practice called “Google dorking.” They can also evade detection during a hacking attempt after reviewing a company’s public assets that describe their cybersecurity defense strategies.
OSINT for cybersecurity
For these reasons, many organizations conduct OSINT assessments of the public sources of information related to their systems, applications and human resources.
The findings can be used to locate unauthorized leaks of proprietary or sensitive data, evaluate information security, and identify vulnerabilities such as unpatched software, misconfigurations or open ports. Organizations can also conduct penetration testing of their systems and networks by using the same OSINT data that are publicly accessible by cybercriminals and hackers.
Often, the information collected during an OSINT assessment is combined with nonpublic data to create a more comprehensive threat intelligence report. Frequent updates to OSINT cybersecurity assessments can help organizations mitigate the risk of data breaches, ransomware, malware and other cyberattacks.
OSINT tools
Because of the vast amount of public information available, it is often impractical to manually collect, sort and analyze OSINT data. Specialized open source intelligence tools can help manage and automate data tasks for various OSINT use cases.
Some OSINT analysis tools use artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect which information is valuable and relevant, and which is insignificant or unrelated. Among the more popular OSINT tools are:
-
Osintframework.com: An extensive directory of free, online OSINT tools and resources hosted on the developer platform GitHub. Both hackers and cybersecurity professionals can use this directory as a starting point to drill down into the specific functionality they seek in an OSINT tool.
-
Maltego: A real-time data mining solution for Windows, Mac and Linux platforms that provides graphic representations of data patterns and connections. With its ability to profile and track the online activities of individuals, this tool can be useful to both cybersecurity professionals and threat actors.
-
Spiderfoot: A data source integration tool for information such as email addresses, phone numbers, IP addresses, subdomains and more. Ethical hackers can use this resource to investigate publicly available information that could pose a threat to an organization or an individual.
-
Shodan: A search engine for internet-connected devices that can also provide information on metadata and open ports. Because this tool can identify security vulnerabilities for millions of devices, it can be useful to both cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals.
-
Babel X: A multilingual, AI-enabled search tool capable of searching the World Wide Web and dark web in more than 200 languages. Security teams within an organization can use this tool to search for sensitive or proprietary information that might be posted on the dark web or in a foreign country.
-
Metasploit: A penetration testing tool that can identify security vulnerabilities in networks, systems and applications. Both cybersecurity professionals and hackers find value in this tool because it can expose the specific weaknesses that can enable a successful cyberattack.
Register for this course: Enrol Now
- Header: A series of bits that contains information about the packet, such as the source and destination IP addresses, the packet's size, and how long it should be forwarded
- Payload: The actual content of the packet, such as an image, video, or text
- How are IP packets used?
- IP packets are used to send and receive data for activities like email, web browsing, and video games. IP packets are a type of datagram, which is a unit of data sent over a packet-switched network
- IP packets can be lost due to network congestion, DDoS attacks, software vulnerabilities, or other factors IP packets can be delivered out of order due to dynamic routing
Register for this course: Enrol Now
